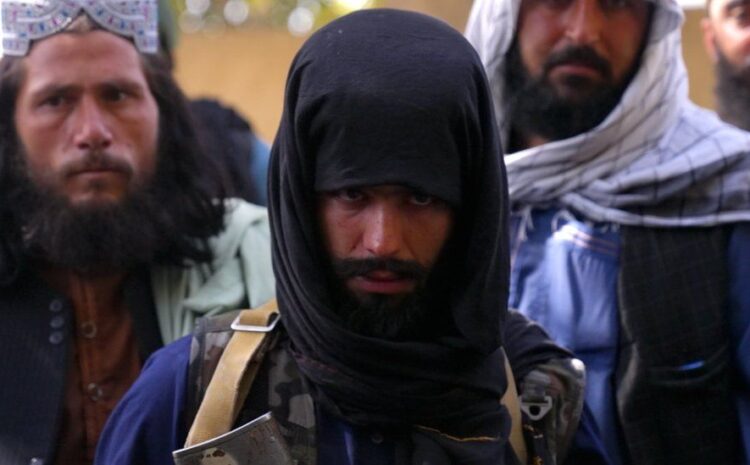

image caption Taliban fighters in Balkh and elsewhere have made a rapid advance in recent weeks
By Secunder Kermani
BBC News, Balkh Province
The “ghanimat” or spoils of war they’re showing off include a Humvee, two pick-up vans and a host of powerful machine guns. Ainuddin, a stony-faced former madrassa (religious school) student who’s now a local military commander, stands at the centre of a heavily-armed crowd.
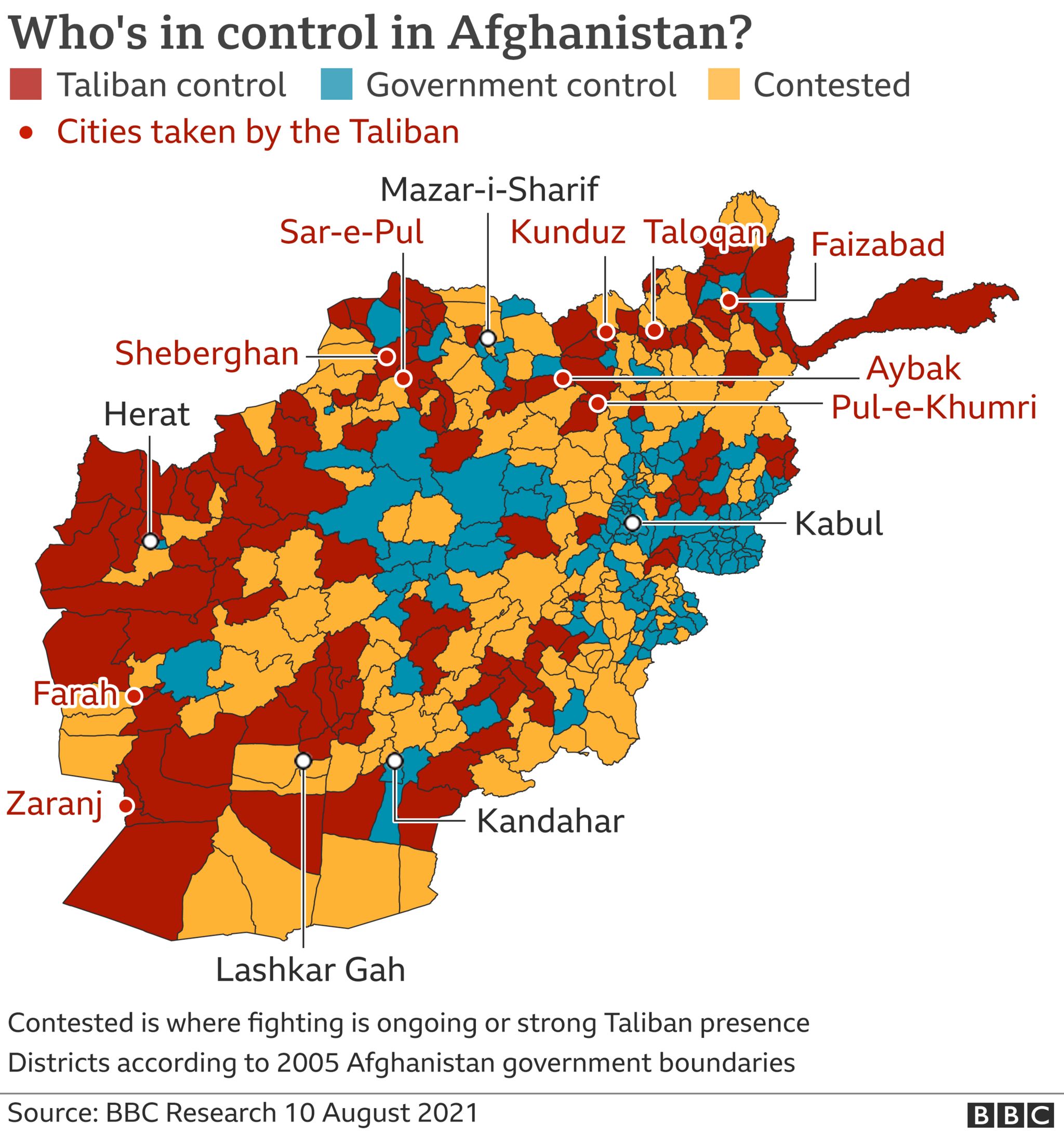
The insurgents have been capturing new territory on what seems like a daily basis as international troops have all but withdrawn. Caught in the middle is a terrified population.
Tens of thousands of ordinary Afghans have had to flee their homes – hundreds have been killed or injured in recent weeks.
I ask Ainuddin how he can justify the violence, given the pain it’s inflicting on the people he claims to be fighting on behalf of?
“It’s fighting, so people are dying,” he replies coolly, adding that the group is trying its best “not to harm civilians”.
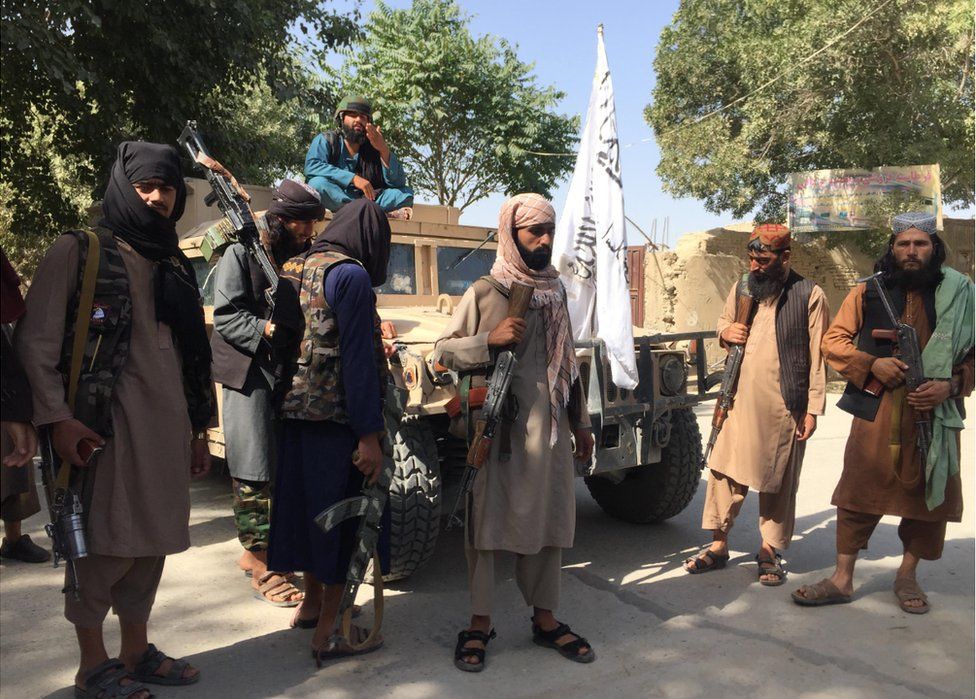

I point out that the Taliban are the ones who have started the fighting.
Ainuddin and the rest of the Taliban feel momentum is with them, and that they are on the cusp of returning to dominance after being toppled by the US-led invasion in 2001.
“They are not giving up Western culture… so we have to kill them,” he says of the “puppet government” in Kabul.
Shortly after we finish speaking we hear the sound of helicopters above us. The Humvee and the Taliban fighters quickly disperse. It’s a reminder of the continuing threat the Afghan air force poses to the insurgents, and that the battle is still far from over.

We’re in Balkh, a town with ancient roots, thought to be the birthplace of one of Islam’s most famous mystic poets, Jalaluddin Rumi.
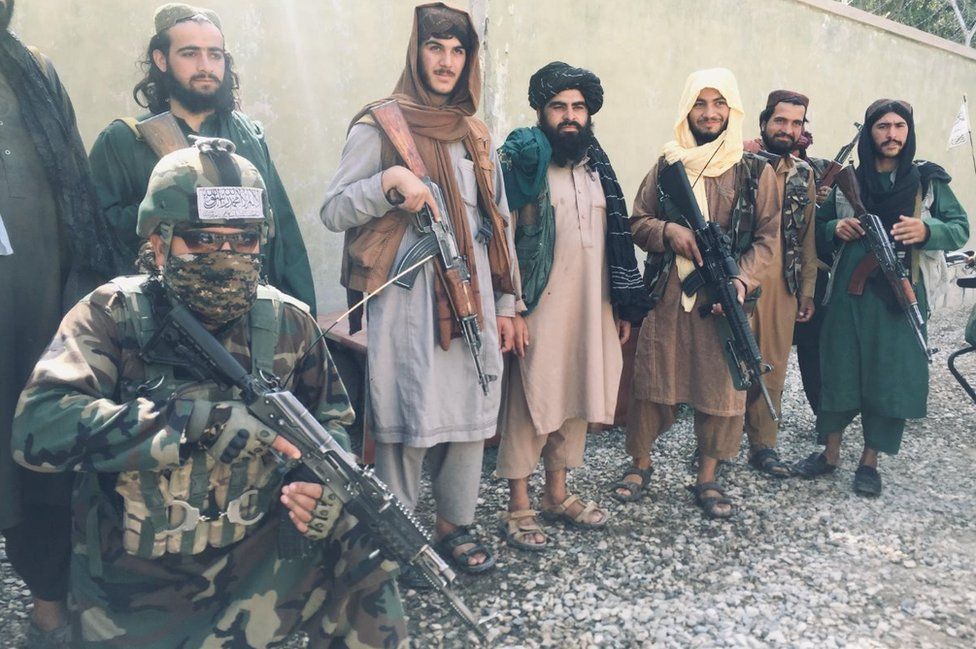

One senior Taliban official said the focus in the north had been deliberate – not only because the region has traditionally seen strong anti-Taliban resistance, but also because it is more diverse.
Despite its core leadership being heavily dominated by members of the Pashtun majority, the official said the Taliban wanted to emphasise they incorporated other ethnicities too.
Haji Hekmat, a local Taliban leader and our host in Balkh, is keen to show us how daily life is still continuing.
The bazaar remains crowded, with both male and female shoppers.
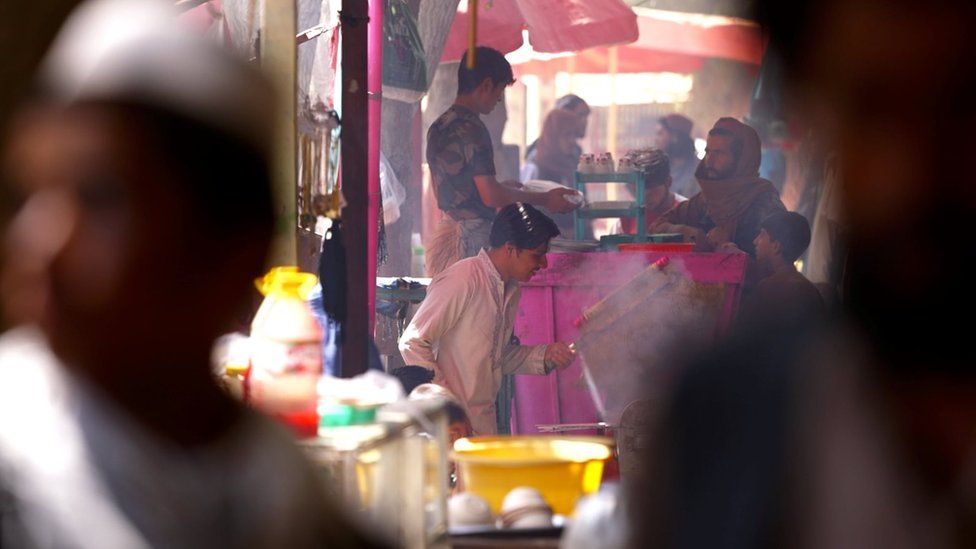

We had been told by local sources that women were allowed to attend only with a male companion, but when we visit that does not seem to be the case. Elsewhere Taliban commanders have reportedly been far stricter.
Haji Hekmat insists no-one is being “forced” and that the Taliban are simply “preaching” that this is how women should dress.
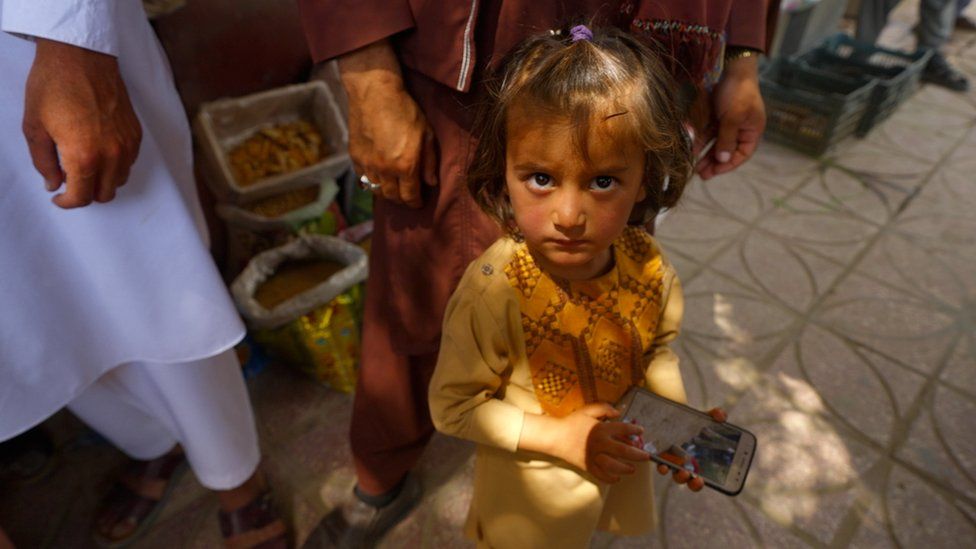

But I’ve been told taxi drivers have been given instructions not to drive any woman into the town unless she’s fully veiled.
The day after we leave, reports emerge of a young woman being murdered because of her clothing. Haji Hekmat, though, rejects allegations Taliban members were responsible.
Many in the bazaar express their support for the group and their gratitude towards them for improving security. But with Taliban fighters accompanying us at all times, it’s difficult to know what residents really think.
The group’s hardline views are at times in tune with more conservative Afghans, but the Taliban are now pushing for control of a number of larger cities.

Find out more on the Afghan conflict 2001-2021
- EXPLAINER: Why is there a war in Afghanistan?
- IN MAPS: How the Taliban retook half of Afghanistan
- PROFILE: Who are the Taliban?
- ANALYSIS: An al-Qaeda resurgence?

In the shadow of Mazar-e-Sharif’s intricately tiled Blue Mosque, men and women strolled around last week in a visibly more relaxed social atmosphere.
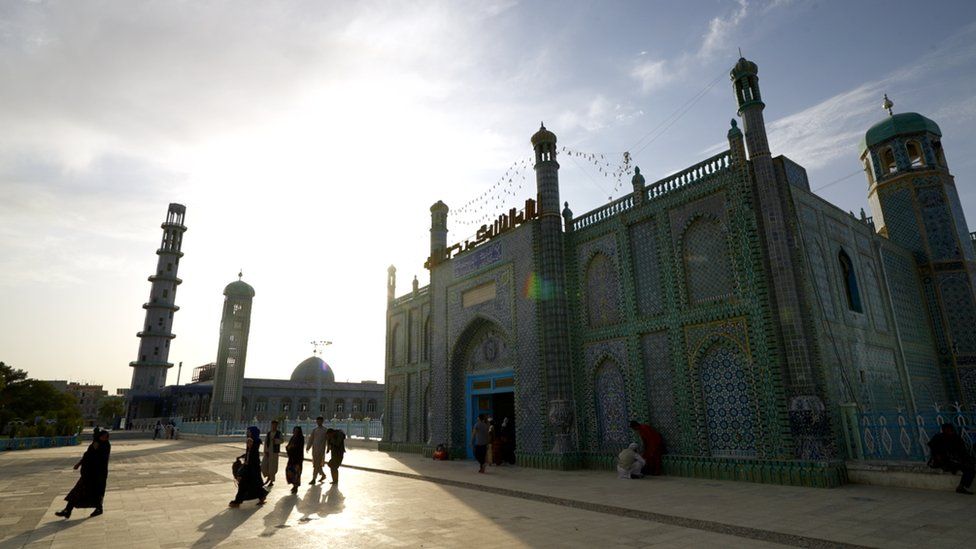

The government are still in control in the city and almost everyone I spoke to expressed concern about what the Taliban’s resurgence will mean, particularly for the “freedoms” younger generations have grown up with.
But back in Balkh district the Taliban are formalising their own rival government. They’ve taken over all the official buildings in the town, bar one large, now abandoned police compound.
It used to be the headquarters of a bitter rival, the local police chief, and was partly destroyed in a suicide bombing by the militants as they fought for control of the area.
The face of the Taliban’s district governor, Abdullah Manzoor, lights up with a broad grin when he talks about the operation, whilst his men chuckle. The fight here, as in so many places in Afghanistan, is deeply personal as well as ideological.
Some things haven’t changed since the Taliban takeover; orange-clad street cleaners are still reporting for work, as are some bureaucrats. They’re overseen by a newly appointed Taliban mayor, seated at a broad wooden desk, with a small white flag of the “Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan” positioned in one corner.
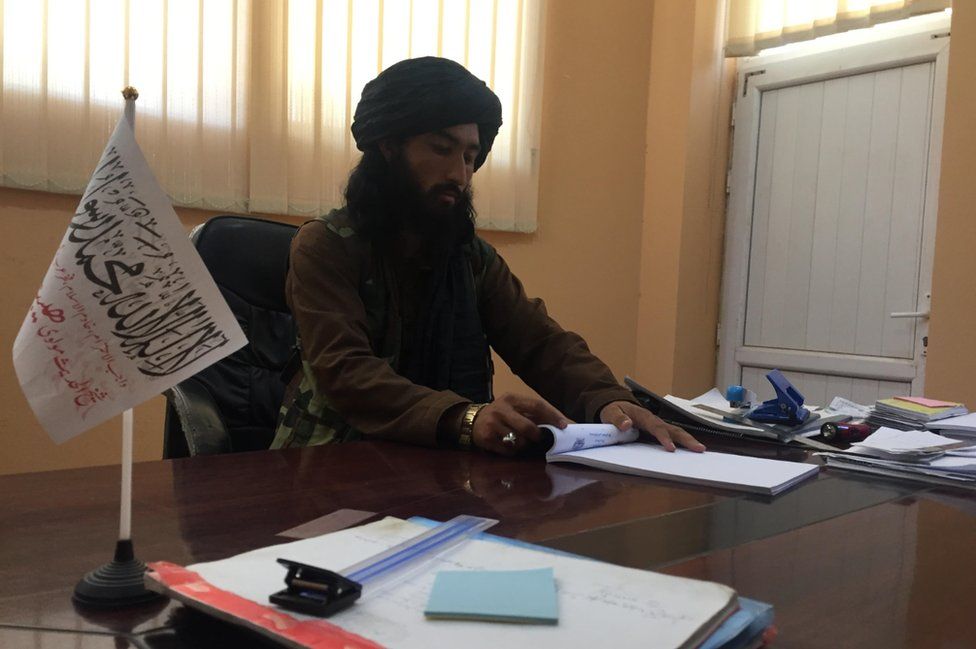

He used to be in charge of ammunition supplies, now it’s taxes – and he tells me proudly the group charges business owners less than the government used to.
The transition from military to civilian life is a work in progress, though. A Taliban fighter still grasping his gun, who moves to pose behind the mayor during our interview, is ushered away by more senior figures.
In other places, however, the insurgents’ hardline interpretation of Islamic scripture is more visible. At the local radio station, they used to play a mixture of Islamic music and general popular hits.
Now it’s only religious chants. Haji Hekmat says they banned music promoting “vulgarity” from being played in public, but insists individuals can still listen to what they want.
I’ve been told, however, of a local man being caught listening to music in the bazaar. To punish him, Taliban fighters are said to have made him walk barefoot in the baking sun, until he lost consciousness.
