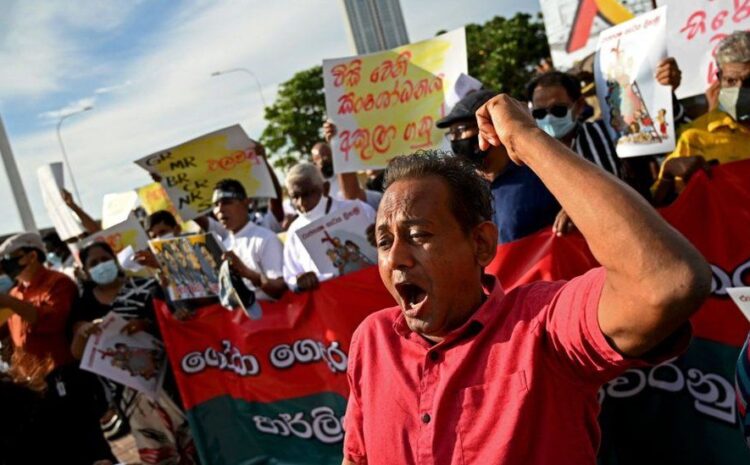
IMAGE SOURCE, GETTY IMAGES Image caption, Sri Lankans took to the streets in early April demanding President Rajapaksa’s resignation
The island nation is facing its worst economic crisis since gaining independence from Britain in 1948 and is facing food shortages, soaring prices and power cuts.
Many say the government is to blame.
Why is there an economic crisis in Sri Lanka?
Sri Lanka’s problems come down to the fact that its foreign currency reserves have virtually run dry.
It means it cannot afford to pay for imports of staple foods and fuel, leading to acute shortages and very high prices.
The government blames the pandemic, which all but killed off Sri Lanka’s tourist trade – one of the island’s biggest foreign currency earners.
However, many experts say economic mismanagement is to blame.
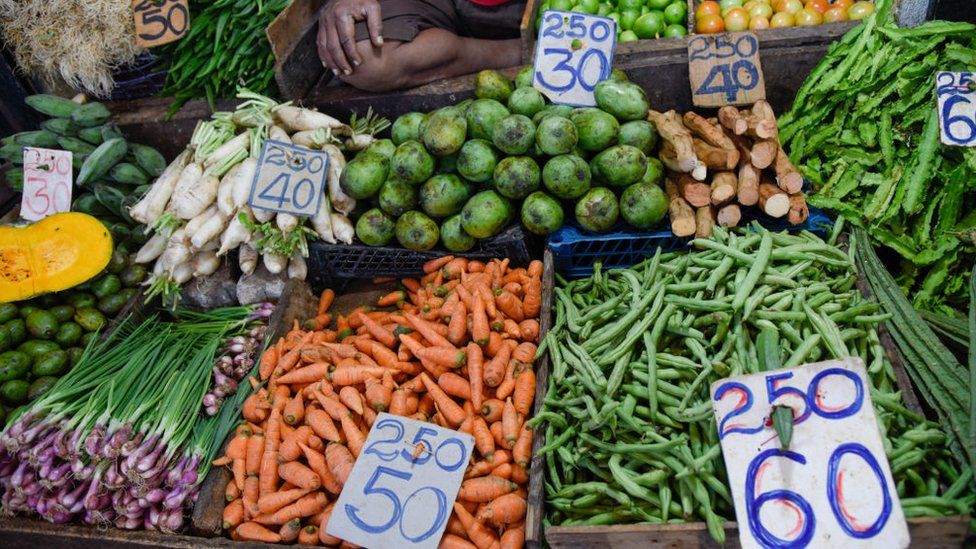 IMAGE SOURCE, GETTY IMAGES
IMAGE SOURCE, GETTY IMAGESThere are many reasons for this, but one main factor is that at the end of its 30-year civil war in 2009, Sri Lanka chose to focus more on its domestic markets instead of exporting to foreign ones. So income from exports remained low, while the bill for imports kept growing.
At the end of 2019, Sri Lanka had $7.6bn (£5.8bn) in foreign currency reserves, but by March 2020 it had only $2.3bn (£1.75bn).
How did the government respond?
When he came to power in 2019, President Rajapaksa decided to cut taxes. This meant the government had less money to buy foreign currency on the international markets to increase its reserves.
This led to widespread crop failures.
Sri Lanka had to supplement its food stocks from abroad, which made its foreign currency shortage even worse.
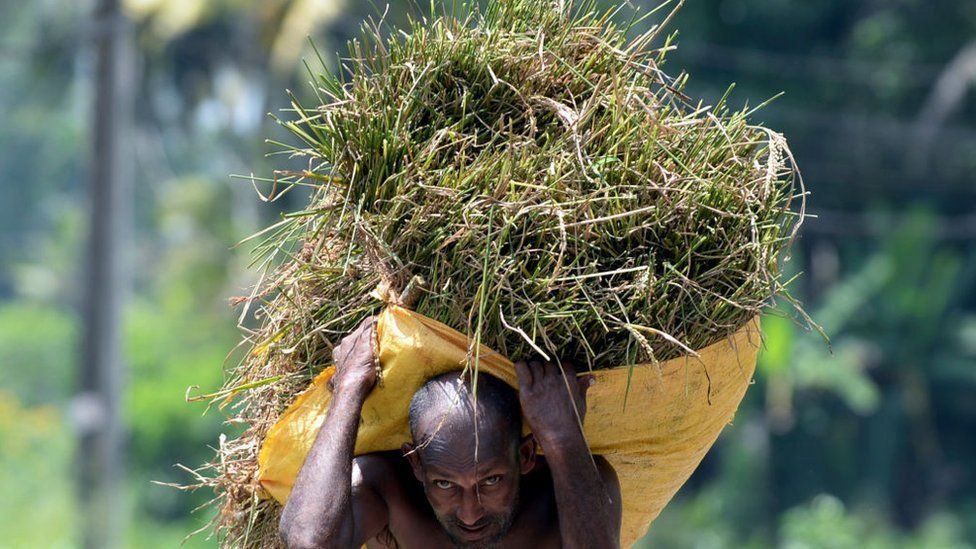 IMAGE SOURCE, GETTY IMAGES
IMAGE SOURCE, GETTY IMAGESSince then, the government has banned the import of a wide range of “non-essential” items – from cars to certain types of food and even shoes.
One way that countries can boost their exports is to cut the value of the currency, but the government refused to let the Sri Lankan rupee fall against other currencies.
It finally did so in March 2022, and the rupee fell more than 30% against the dollar.
How much foreign debt must Sri Lanka repay?
Sri Lanka’s government has to raise $7bn in foreign currency this year to pay down its debt. It will have to make similar payments for years to come.
The government would like to make new finance deals to settle its debts, but its credit rating has fallen so low that very few institutions will lend it money. As a result, it has been running down its foreign reserves simply to pay the interest on the current loans.
What is the political situation?
Mass protests flared up in early April with people calling for President Rajapaksa to resign, which he has refused to do.
People are furious because the cost of living has become unaffordable. They are paying up to 30% more for food compared with a year earlier, which has led to some people having to cut down not only on what food they buy, but also the number of meals they eat every day.
Shortages of fuel have seen long lines at petrol stations, while the crisis has also hit public transport services.
“Earlier I used to get a bus in 15 minutes, now I have to wait one to two hours. Sometimes the bus stops midway with no fuel,” one woman told the BBC.
 IMAGE SOURCE, GETTY IMAGES
IMAGE SOURCE, GETTY IMAGESAs demonstrations grew, the president imposed a curfew, a draconian emergency law and a ban on social media. However, when these failed to keep protesters off the streets, he withdrew the measures.
President Rajapaksa then sacked everyone in his cabinet apart from the prime minister, Mahinda Rajapaksa, who is his brother. He also sacked the governor of the central bank.
The new finance minister he appointed resigned less than 24 hours after taking the job.
The president asked opposition MPs to help form a new government, but they have refused. Instead, more than 40 MPs aligned to the ruling coalition in parliament have left it.
What help can Sri Lanka get from abroad?
In March, Sri Lanka’s government asked the International Monetary Fund (IMF) for a bailout.
The new central bank governor, P Nandalal Weerasinghe, will lead the negotiations between the government and the IMF. However, the talks have had to be postponed until a new finance minister is found.
Meanwhile, Sri Lanka is being helped by friendly neighbours such as India. It has begun supplying fuel to Sri Lanka on a $500m credit line.
China has agreed to bolster Sri Lanka’s foreign currency reserves by swapping the Lankan rupee for its currency, the renminbi.
It has also taken loans from countries like Japan and Bangladesh.
-
Why are there food queues in this Indian Ocean island?
20 September 2021
-
How soaring cost of living is hitting Sri Lanka hard
12 January
-
Tear gas and water cannon at Sri Lanka protests
3 April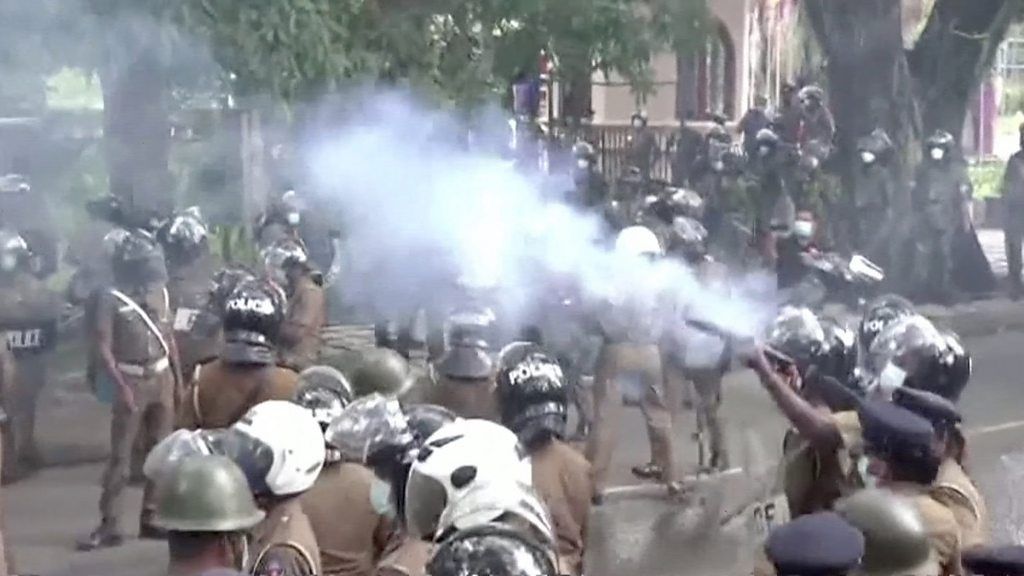
-
Sri Lanka profile
18 November 2019