
IMAGE COPYRIGHT REUTERS image caption Naftali Bennett (right) ended Benjamin Netanyahu’s long tenure in office
A new “government of change” will be led by right-wing nationalist Naftali Bennett of the Yamina party.
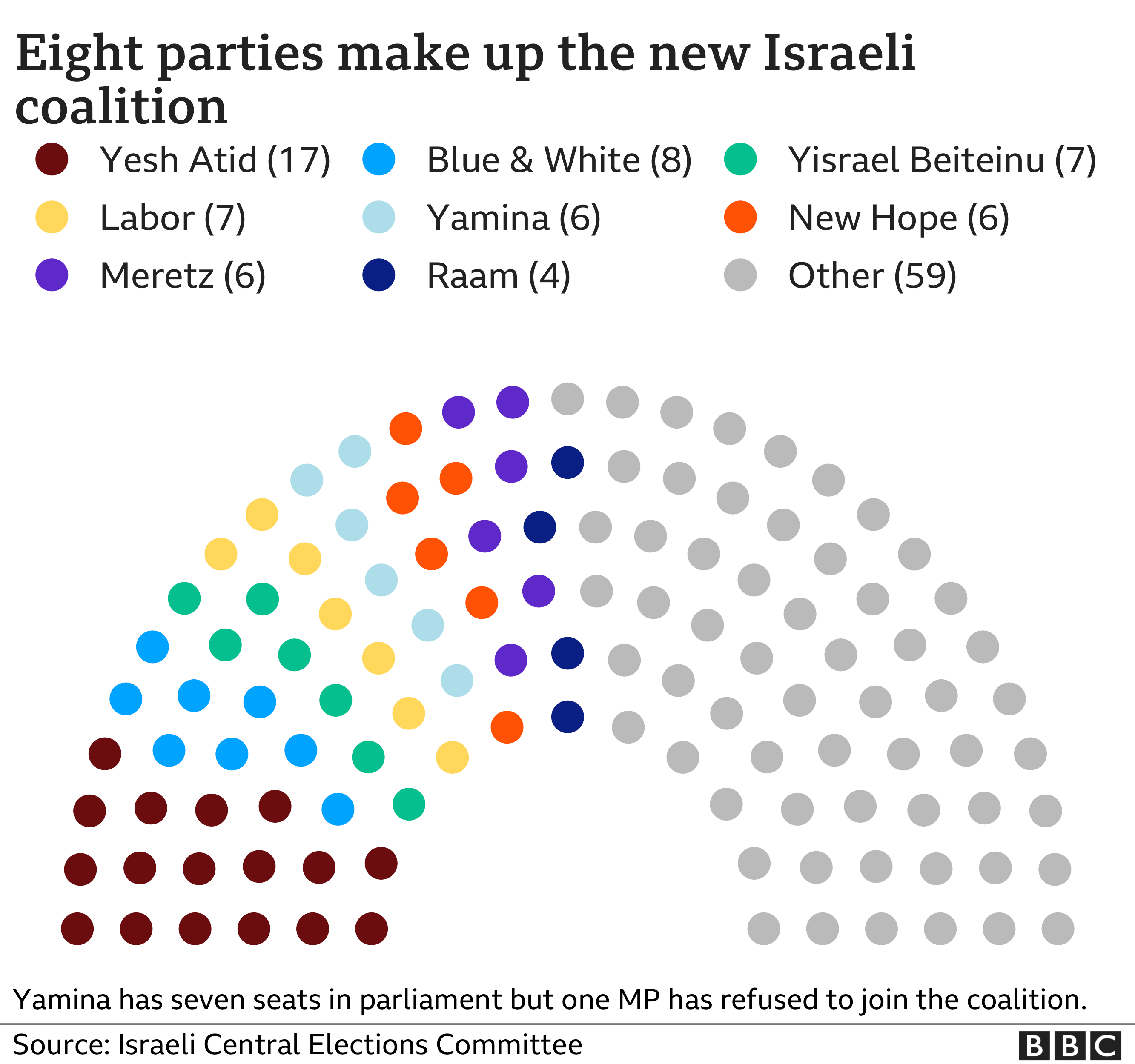
He will lead an unprecedented coalition of parties which was approved with a razor-thin majority of 60-59.
Mr Bennett will be prime minister until September 2023 as part of a power-sharing deal.
He will then hand power over to Yair Lapid, leader of the centrist Yesh Atid, for a further two years.
Mr Netanyahu – Israel’s longest-serving leader who has dominated its political landscape for years – will remain head of the right-wing Likud party and become leader of the opposition.
During the debate in the Knesset (parliament), a defiant Mr Netanyahu promised: “We’ll be back.”
US President Joe Biden has already sent his congratulations to Mr Bennett, saying he looks forward to working with him.
Why has this happened?
Mr Netanyahu has served a record-breaking five terms, first from 1996 to 1999, then continuously from 2009 to 2021.
He called an election in April 2019 but failed to win enough support to form a new coalition government. Two more elections followed, each of which ended inconclusively.
The third election resulted in a government of national unity where Mr Netanyahu agreed to share power with the then-opposition leader Benny Gantz. But the arrangement collapsed in December, triggering a fourth election.
Although Likud emerged as the largest party in the 120-seat Knesset, Mr Netanyahu was again unable to form a governing coalition and the task was handed to Mr Lapid, whose centrist Yesh Atid party had emerged as the second largest.
Opposition to Mr Netanyahu staying in power had grown, not just among the left and centre but also among right-wing parties that are ordinarily ideologically aligned to Likud, including Yamina.
Although Yamina came joint fifth in the election with only seven seats, its support was critical if any potential coalition government was to have a majority in parliament. After weeks of negotiations, Mr Lapid brought Yamina on board as part of a constellation of parties whose only common goal was to remove Mr Netanyahu from office.
The agreement involving eight factions with the 61 seats required for a majority was signed on 2 June, just half an hour before a deadline was due to expire, effectively sealing Mr Netanyahu’s fate.
What will the new government be like?
In appearance, Mr Bennett’s government will be unlike any which has preceded it in Israel’s 73-year history.
The alliance contains parties which have vast ideological differences, and perhaps most significantly includes the first independent Arab party to be part of a potential ruling coalition, Raam. It is also expected to have a record number of eight female ministers.

The inclusion of Raam and left-wing non-Arab Israeli parties means there could be friction on issues such as Israeli policies towards Palestinians – Yamina and another right-wing party, New Hope, are staunch supporters of Jewish settlement in the Israeli-occupied West Bank, for instance.
In addition, some parties want to relax religious restrictions more extensively than Yamina – a national-religious party – will likely allow.
Mr Bennett has indicated his government would focus on areas where agreement was possible, like economic issues or the coronavirus pandemic, while avoiding more contentious matters.
“Nobody will have to give up their ideology,” he recently said, “but all will have to postpone the realisation of some of their dreams… We’ll focus on what can be achieved, rather than arguing about what cannot.”
